-
[WWDC19] Advances in UI Data SourcesiOS 2022. 6. 27. 11:48
Advances in UI Data Sources - WWDC19 - Videos - Apple Developer
Use UI Data Sources to simplify updating your table view and collection view items using automatic diffing. High fidelity, quality...
developer.apple.com
Current state-of-the-art
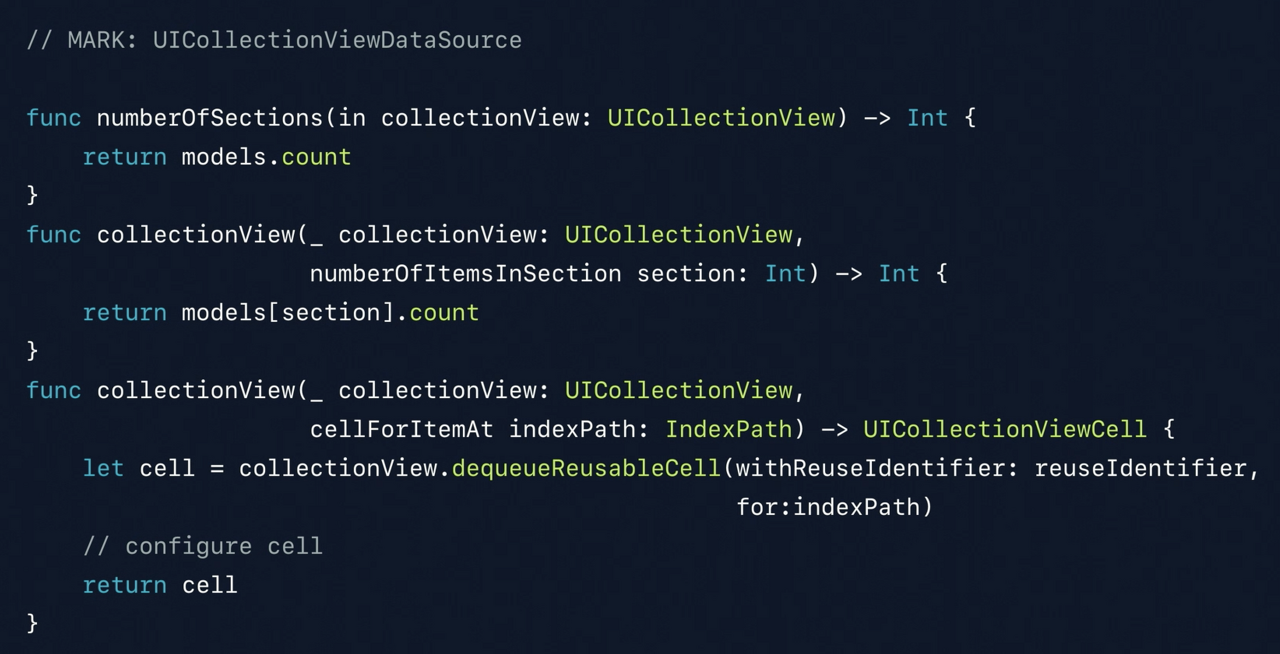
당시
UICollectionViewdata source를 구현하기 위해서는 위와 같이 구현해야 했다.- 섹션의 수
- 각 섹션 내의 아이템의 수
를 제공하고 있다. 만약 1차원 혹은 2차원 data source를 가지고 작업한다면 특징은 아래와 같다.
- Simple : 단순히 배열 내 요소를 iterate 한다
- Flexible : data source에 정해진 타입이 없다.

하지만 1차원, 2차원 배열보다 더 복잡한 경우가 있다. 앱들은 점점 더 복잡해지고, 기능 요구사항도 많아진다.
- data source가 앱 내의 복잡한 controller에 의해 뒷받침 될 때가 있다.
- 복잡한 controller는 다양한 작업을 한다.
- Core data와 상호작용하고, 웹 서비스를 이용할 수 있다.
Conversation between UI layer and Controller
Controller layer는 데이터를 가져오기 위한 복잡한 작업들을 한다.
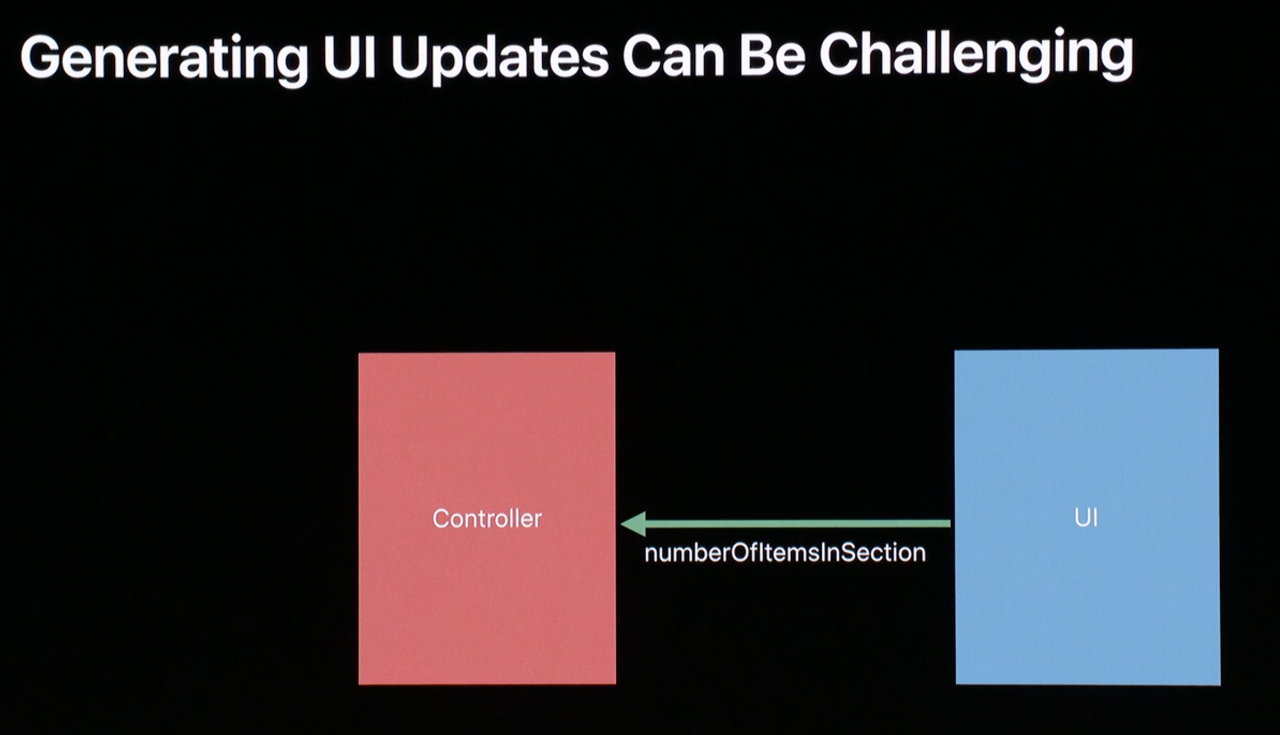
UI layer가 Controller layer에 화면에 출력할 데이터나 cell을 요청한다.
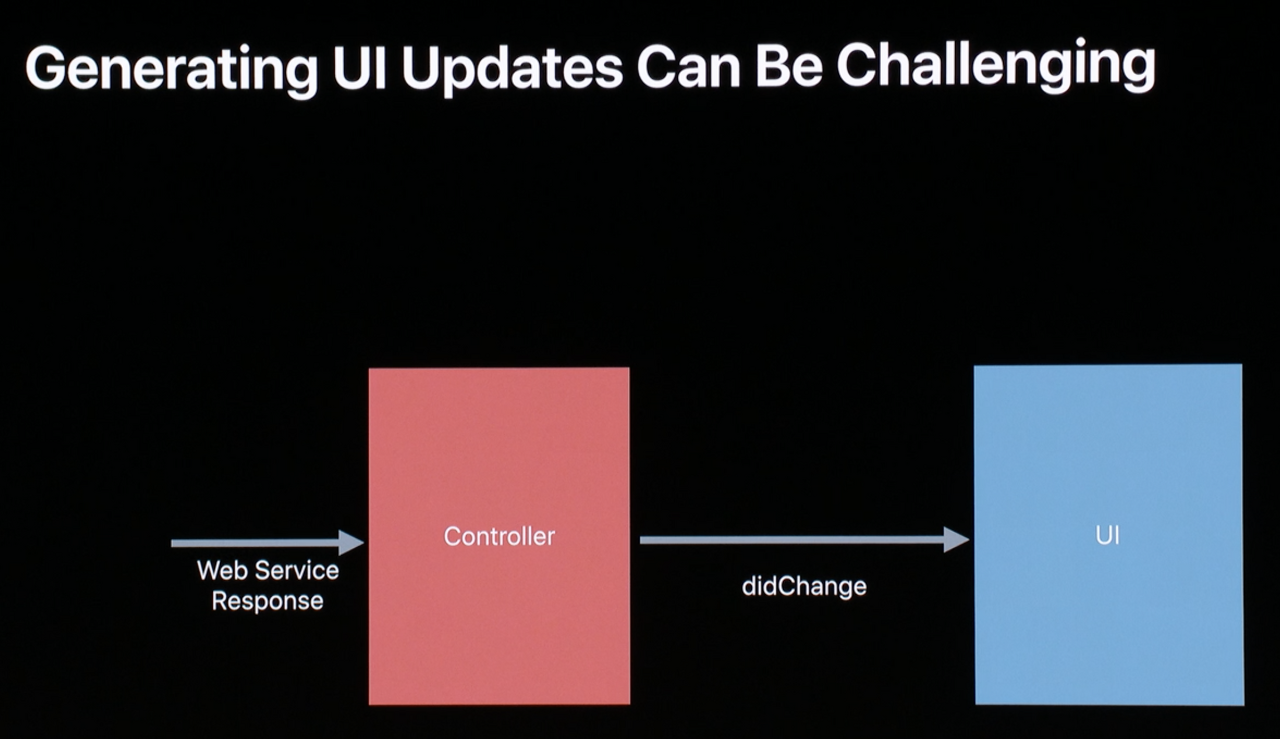
더 복잡한 경우를 생각해보자.
- Controller가 웹 서비스 요청 후 응답을 받았다.
- Controller가 자신이 변했음(자신 내부의 무언가가 변했음)을 알린다.
- UI layer가 무언가가 변했음을 알고 업데이트를 한다.
Imperfect world
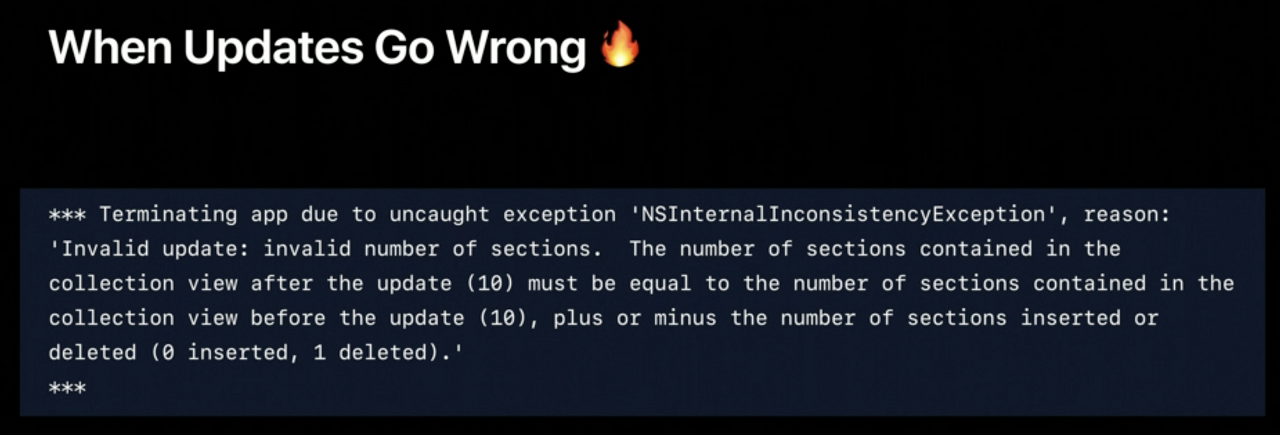
Batch 업데이트를 에러 없이 수행하기 위해 노력해도 안 되는 경우가 있다. 개발하며 위와 같은 에러를 마주한 적이 있을 것이다. 이를 해결하기 위해
reloadData를 호출하면 애니메이션 없이 reload가 수행된다.Where is our truth?

문제는 "truth"가 어디있냐는 것이다. 여러 군데에서 업데이트가 발생하고 데이터가 업데이트 됐을 때 layer 별로 특정 시간대에 다른 정보를 가질 수 있다. 이 때 정답은 누가 가지고 있느냐가 문제인 것이다.
- 위 상황에서 문제는 data controller(data source)가 시간마다 변하는 자신만의 truth를 가진다는 것이다. 그리고 UI도 자신만의 truth를 가지고 있다.
truth는 하냐여야 하는데 data고 ui고 자신만의 truth를 가지고 있으니 문제가 된다. - UI layer 코드는 이 두 버전의 truth가 항상 동기화되어야 하는 것에 대한 책임이 있다. 하지만 위 에러에서도 봤듯이 어려운 상황이 있다. 따라서 이런 접근 방식은 에러가 발생하기 쉽다.
- 즉 Centralized truth가 없다는 것이 문제가 된다.
A new approach

새로운 접근 방식인 DiffableDataSource가 등장했다.

DiffableDataSource는
performBatchUpdates가 없다. : 모든 crash, hassle, 복잡도가 없어졌다.apply메서드가 생겼다. : 간단하고, 자동적이고, hassle이 없는 diffing(차이를 적용하는 작업)이다.
Snapshot

Snapshot이라는 새로운 구조를 사용할 것이다.
- 현재 UI 상태의 truth다.
IndexPath대신, 유일한 섹션 식별자와 아이템 식별자를 가지고 있다.IndexPath대신 아이템 식별자로 업데이트한다.
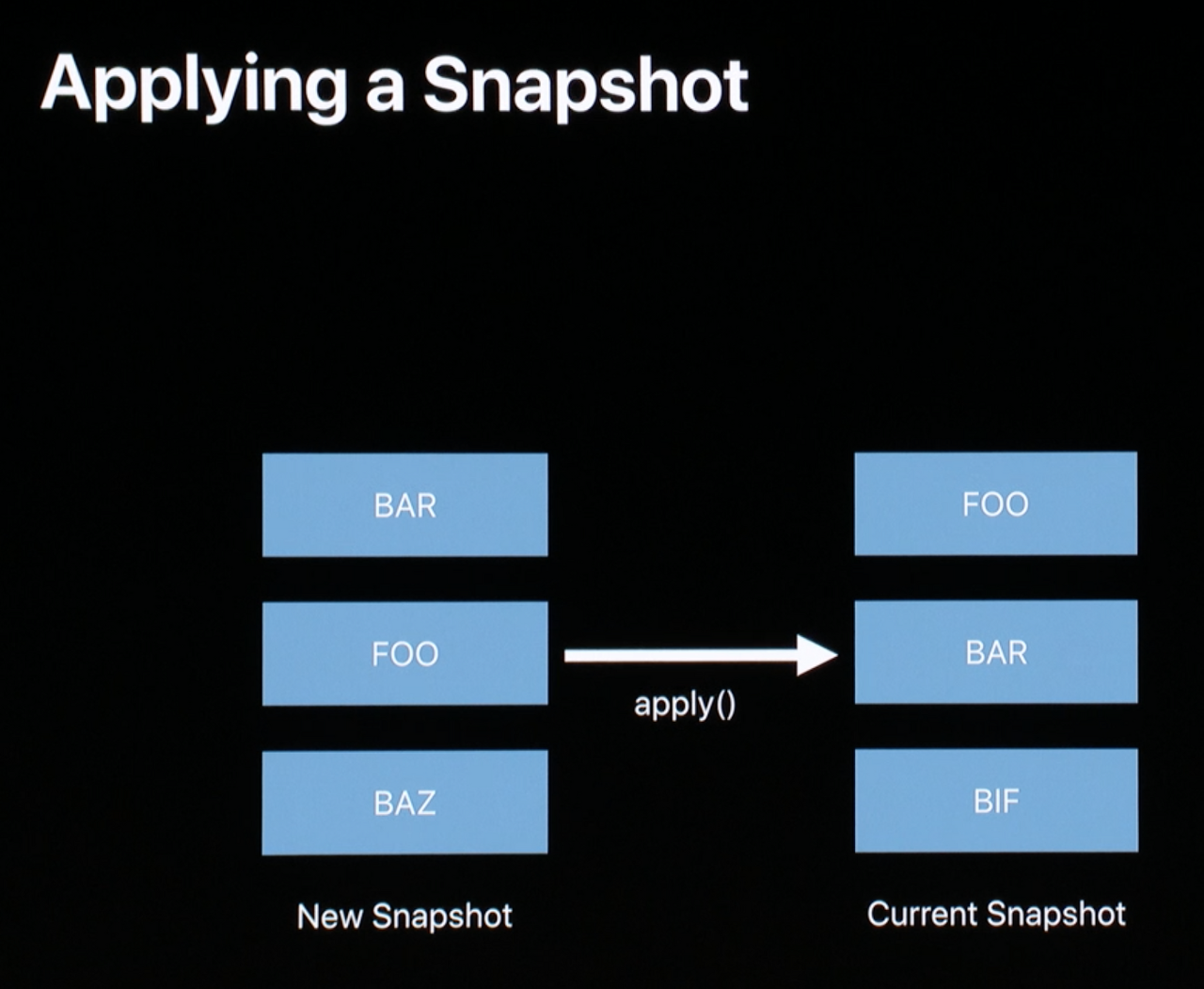
- 현재 화면에 FOO, BAR, BIF를 식별자로 가진 것들이 출력되고 있다고 하자.
- Controller가 변했다. 왼쪽의 새로운 snapshot을 적용하고 싶다.
apply()를 통해 새로운 상태를 현재 상태에 반영한다.
Diffable Data Source

모든 플랫폼에 4개의 클래스가 있다.
- iOS, TVoS :
UICollectionViewDiffableDataSource,UITableViewDiffableDataSource - mac :
NSCollectionViewDiffableDataSource
모든 플랫폼에 현재 UI 상태에 대한 책임이 있는
NSDiffableDataSourceSnapshot가 있다.Demos
3단계 작업으로 이루어진다.
- 변화가 생긴 후, snapshot을 생성한다. 변화를 collectionView나 tableView에 적용하기 위한 Snapshot이다.
- Snapshot에 업데이트 사이클에 출력하고 싶은 아이템들에 대한 내용을 포함시킨다.
apply()를 통해 UI를 자동으로 바꾼다.
DiffableDataSource는 차이와 변화를 UI에 반영하는 것들을 관리해준다.
Demo 1
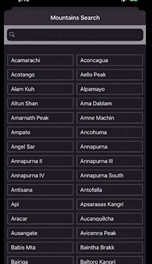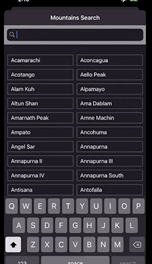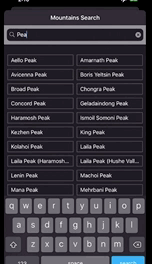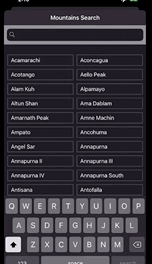
산 이름을 검색할 수 있는 앱이다. 검색창에 검색어를 입력할때마다 하단에 나오는 산의 목록이 자동으로 업데이트 된다.

1. Snapshot 생성
var snapshot = NSDiffableDataSourceSnapshot<Section, MountainsController.Mountain>()Snapshot은 Swift의 제네릭 클래스다. 사용하고자 하는
SectionIdentifierType과ItemIdentifierType을 파라미터로 가지고 있다.여기에서 사용된 section, item identifier type을 보자.
SectionIdentifierType
enum Section: CaseIterable { case main }하나의 섹션만 필요할 때 위와 같이 enum으로 만들어주면 유용하다. Enum이 좋은 것은 자동으로 hashable 하다는 것이다. 그래서 하나의 case가 있는 enum을 생성해서 SectionIdentifierType을 만들었다.
ItemIdentifierType
struct Mountain: Hashable { let name: String let height: Int let identifier = UUID() func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) { hasher.combine(identifier) } static func == (lhs: Mountain, rhs: Mountain) -> Bool { return lhs.identifier == rhs.identifier } func contains(_ filter: String?) -> Bool { guard let filterText = filter else { return true } if filterText.isEmpty { return true } let lowercasedFilter = filterText.lowercased() return name.lowercased().contains(lowercasedFilter) } }Mountainstruct를 생성했다. 이 구조체가 hashable하게 해서 identifier를 명시적으로 전달하는 대신 사용할 수 있게 했다. 중요한 것은 각 mountain이 hash 값에 의해 식별돼서 DiffableDataSource에서 사용할 수 있다는 것이다.
위 코드에서는 hash 값으로 identifier를 그냥 제공하고 있다. 이 identifier는 DiffableDataSource가 이전에서 다음으로 업데이트 할 때 바뀐 게 무엇인지를 추적하기 위해 사용할 수 있는 식별자다.
그래서 모든 mountain은 고유한 identifier를 가지고 있어야 한다.2. 다음 업데이트에 출력하고 싶은 아이템의 identifier 추가
snapshot.appendSections([.main]) snapshot.appendItems(mountains)snapshot은 처음에 완전 비어있는 상태이기 때문에 여기에 우리가 원하는 섹션과 아이템을 추가해야 한다. 이 경우 하나의 섹션만 필요하기 때문에main이라는 섹션 하나를 추가했다.그리고 아이템들의 identifier를 추가했다. 주로 여기에서는 identifier의 배열을 전달한다. Swift에서는 여기에 내 커스텀 타입을 사용할 수 있다.
Native 타입(struct, enum과 같은 값 타입도 포함)을 hashable하게 만들면 객체 자체를 전달할 수 있다.
3. apply
dataSource.apply(snapshot, animatingDifferences: true)Snapshot을 적용한다. 이러면 DiffableDataSource는 자동으로 이전 업데이트에서 어떤 것이 바뀌는지 찾는다.
- idexPath : fragile, ephemeral. 특정 업데이트를 참조하고, 다른 의미와 다른 업데이트를 갖는다.
- identifier : robust, enduring. 간단하다.
collectionView와 연결
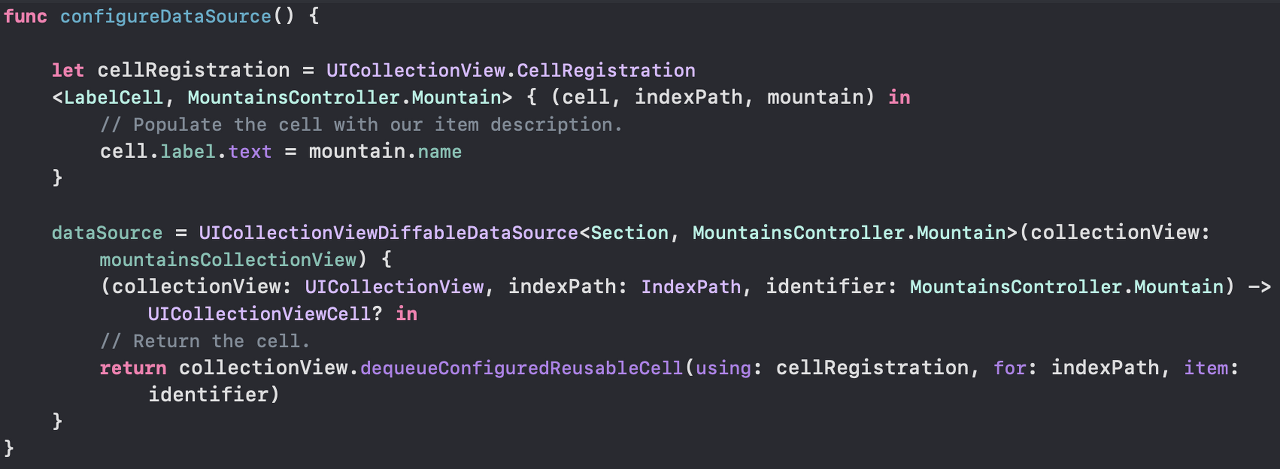
configureDataSource라는 메서드를 생성해서 datasource를 설정했다. UICollectionView로 작업하고 있기 때문에 UICollectionViewDiffableDataSource 객체를 만들었다. 여기에 섹션, 아이템 타이템 타입을 인자로 전달했다.dataSource = UICollectionViewDiffableDataSource<Section, MountainsController.Mountain>(collectionView: mountainsCollectionView) { (collectionView: UICollectionView, indexPath: IndexPath, identifier: MountainsController.Mountain) -> UICollectionViewCell? in // Return the cell. return collectionView.dequeueConfiguredReusableCell(using: cellRegistration, for: indexPath, item: identifier) }같이 사용하고자 하는 collectionView를 가리키는 포인터를 전달한다. DiffableDataSource는 이 포인터를 받아 해당 collectionView를 위한 data source로서 자신을 연결한다.
클로저 안에 있는 부분은
cellForItemAt IndexPath메서드를 구현할 때 작성하던 부분과 비슷하다. CollectionView에 출력하고자 하는 적절한 cell과 데이터를 받는다.여기에서 편리한 점은 아이템의 IndexPath를 사용하지 않고 identifier를 사용해서(여기에서는 native Swift 값 타입을 사용해서) 우리가 출력하고 싶은 아이템을 표시한 것이다.
let cellRegistration = UICollectionView.CellRegistration<LabelCell, MountainsController.Mountain> { (cell, indexPath, mountain) in // Populate the cell with our item description. cell.label.text = mountain.name }위
cellRegisteration을 사용해서 cell이 주어졌을 때 데이터를 어떻게 바인딩할지를 나타냈다.Demo 2

iOS의 와이파이 설정 부분을 mockup 한 것이다. 이전 데모와 다른 점은 섹션이 두개라는 것이다.
- config section : 상단 섹션. 와이파이를 끄거나 킬 수 있다. 와이파이를 끄면 하단 섹션이 화면에 나타나지 않는다.
- wifi section : 하단 섹션. 현재 연결할 수 있는 네트워크들이 계속 동적으로 업데이트 되며 나타난다.
여기도 마찬가지로 세 단계로 이루어진다.
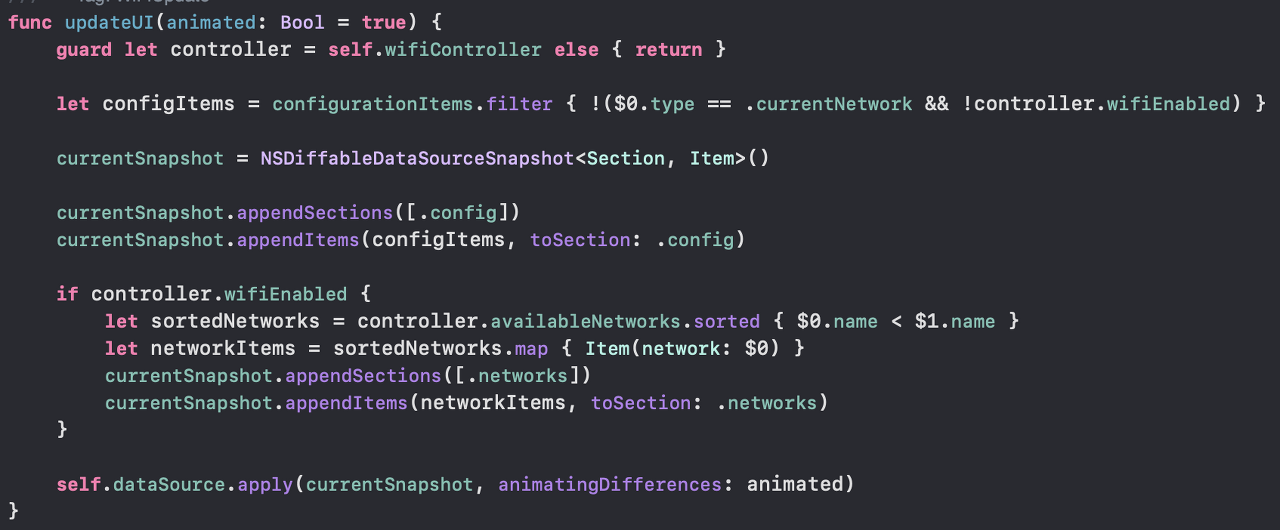
1. Snapshot 생성
let configItems = configurationItems.filter { !($0.type == .currentNetwork && !controller.wifiEnabled) } currentSnapshot = NSDiffableDataSourceSnapshot<Section, Item>()출력하고 싶은 데이터를 받는다. 그리고 Snapshot을 생성한다. 이 Snapshot은 초기에 비어있는 상태이기 때문에 우리가 출력하고 싶은 부분으로 snapshot을 구성해야 한다.
SectionIdentifierType
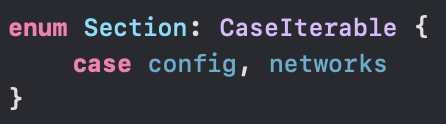
섹션을 enum으로 생성해서 자동으로 hashable하게 만들었다.
ItemIdentifierType
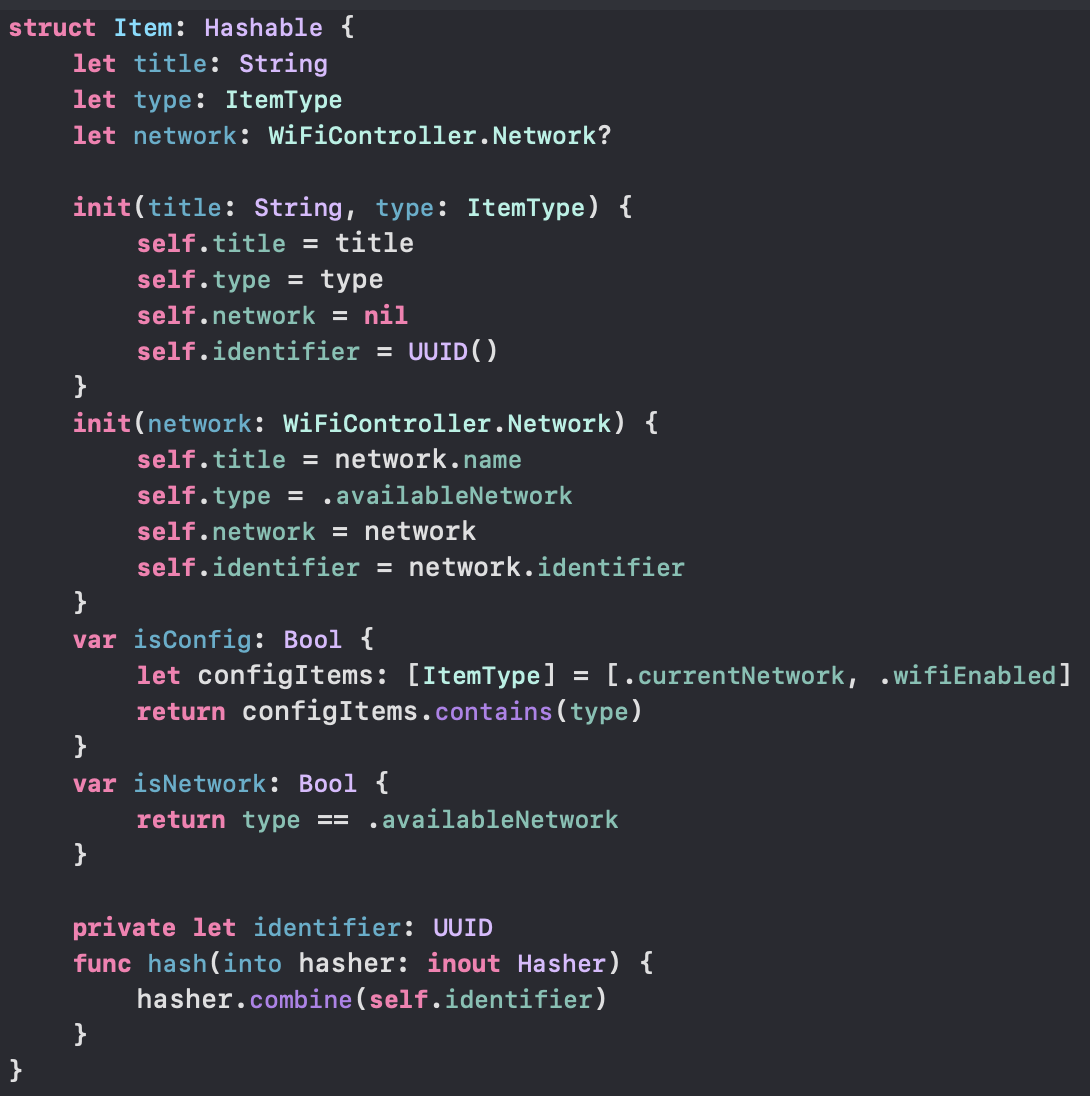
Demo 1의 Mountain과 비슷하게, hashable한 struct를 만들었다. hash 함수에서는 고유한 identifier 값을 기반으로 연산하고 있어서 각 아이템을 구별할 수 있게 해준다.
2. 다음 업데이트에 출력하고 싶은 아이템의 identifier 추가
currentSnapshot.appendSections([.config]) currentSnapshot.appendItems(configItems, toSection: .config) if controller.wifiEnabled { let sortedNetworks = controller.availableNetworks.sorted { $0.name < $1.name } let networkItems = sortedNetworks.map { Item(network: $0) } currentSnapshot.appendSections([.networks]) currentSnapshot.appendItems(networkItems, toSection: .networks) }먼저 상단의 config 섹션을 추가하고 아이템을 추가한다.
와이파이가 활성화되어 있으면 model layer에 연결 가능한 와이파이 목록을 요청한다. 네트워크 섹션을 추가하고, 모델 레이어에서 받은 아이템을 해당 섹션에 추가한다.
우리가 아이템을 추가할 섹션을 명시적으로 나타낼 수 있다.이제 화면에 출력하고 싶은 모든 것을 다 작성했다.
3. apply
self.dataSource.apply(currentSnapshot, animatingDifferences: animated)DiffableDataSource에게 변화를 적용할 것을 요청했다.
collectionView와 연결
자세히 볼 필요는 없다. Demo1에서 한 것과 크게 다르지 않은데, 코드가 긴 것은 셀 타입에 따라 cell을 구성하는 코드가 길기 때문이다.
func configureDataSource() { wifiController = WiFiController { [weak self] (controller: WiFiController) in guard let self = self else { return } self.updateUI() } self.dataSource = UITableViewDiffableDataSource <Section, Item>(tableView: tableView) { [weak self] (tableView: UITableView, indexPath: IndexPath, item: Item) -> UITableViewCell? in guard let self = self, let wifiController = self.wifiController else { return nil } let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell( withIdentifier: WiFiSettingsViewController.reuseIdentifier, for: indexPath) var content = cell.defaultContentConfiguration() // network cell if item.isNetwork { content.text = item.title cell.accessoryType = .detailDisclosureButton cell.accessoryView = nil // configuration cells } else if item.isConfig { content.text = item.title if item.type == .wifiEnabled { let enableWifiSwitch = UISwitch() enableWifiSwitch.isOn = wifiController.wifiEnabled enableWifiSwitch.addTarget(self, action: #selector(self.toggleWifi(_:)), for: .touchUpInside) cell.accessoryView = enableWifiSwitch } else { cell.accessoryView = nil cell.accessoryType = .detailDisclosureButton } } else { fatalError("Unknown item type!") } cell.contentConfiguration = content return cell } self.dataSource.defaultRowAnimation = .fade wifiController.scanForNetworks = true }위에서 클로저 안에 존재하는 긴 코드는 diffableDataSource를 사용하지 않더라도
cellForItem IndexPath메서드 안에 존재했을 코드다.Demo 3
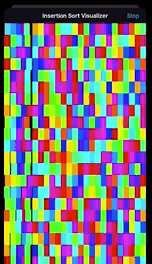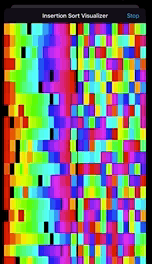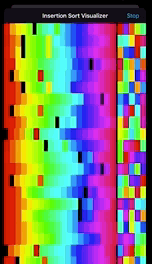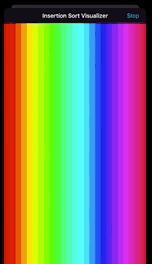
처음에 색이 랜덤하게 존재하는데, sort 버튼을 누르면 무지개 순으로 색이 정렬된다. 이전 데모와 다른 점은 초기의 랜덤한 상태에서, 최종 상태(무지개)로 바로 건너뛰는 것이 아니라,
각 정렬 과정을 중간에 볼 수 있다는 것이다. 즉 초기 상태에서 바로 최종 상태로 건너 뛰는 것이 아니라, 각 단계마다 정렬되는 과정을 UI에 반영해야 한다는 것이다.
이에 맞게 각 정렬 순간마다 Snapshot을 생성하고 적용해야 한다.Demo 3에서 3단계를 진행하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
func performSortStep() { if !isSorting { return } var sectionCountNeedingSort = 0 // Get the current state of the UI from the data source. var updatedSnapshot = dataSource.snapshot() // For each section, if needed, step through and perform the next sorting step. updatedSnapshot.sectionIdentifiers.forEach { let section = $0 if !section.isSorted { // Step the sort algorithm. section.sortNext() let items = section.values // Replace the items for this section with the newly sorted items. updatedSnapshot.deleteItems(items) updatedSnapshot.appendItems(items, toSection: section) sectionCountNeedingSort += 1 } } var shouldReset = false var delay = 125 if sectionCountNeedingSort > 0 { dataSource.apply(updatedSnapshot) } else { delay = 1000 shouldReset = true } let bounds = insertionCollectionView.bounds DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + .milliseconds(delay)) { if shouldReset { let snapshot = self.randomizedSnapshot(for: bounds) self.dataSource.apply(snapshot, animatingDifferences: false) } self.performSortStep() } }1. Snapshot 생성
// Get the current state of the UI from the data source. var updatedSnapshot = dataSource.snapshot()이전 Demo들에서는 새로운 snapshot을 생성했는데, 여기에서는 현재 snapshot을 가져왔다. 이 snapshot은 현재 UICollectionView가 보여지고 있는, 가지고 있는 현재의 truth가 된다.
이렇게 하는 이유는 우리는 정렬되는 모든 과정을 다 보여줘야 하기 때문이다. 이를 통해 완전히 새로 시작하지 않고 중간 상태에서 시작해서 다음 상태로 넘어갈 수 있다.2. 다음 업데이트에 출력하고 싶은 아이템의 identifier 추가
// For each section, if needed, step through and perform the next sorting step. updatedSnapshot.sectionIdentifiers.forEach { let section = $0 if !section.isSorted { // Step the sort algorithm. section.sortNext() let items = section.values // Replace the items for this section with the newly sorted items. updatedSnapshot.deleteItems(items) updatedSnapshot.appendItems(items, toSection: section) sectionCountNeedingSort += 1 } }appendItems,deleteItems등 snapshot을 수정할 수 있는 다양한 함수들이 존재한다. 이들을 사용해서 item들의 순서를 바꿀 수 있다.
여기에서도 이전 데모들과 마찬가지로 indexPath가 아닌 identifier를 사용해서 우리가 원하는 새로운 상태로 snapshot을 설정한다.3. apply
var shouldReset = false var delay = 125 if sectionCountNeedingSort > 0 { dataSource.apply(updatedSnapshot) } else { delay = 1000 shouldReset = true } let bounds = insertionCollectionView.bounds DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + .milliseconds(delay)) { if shouldReset { let snapshot = self.randomizedSnapshot(for: bounds) self.dataSource.apply(snapshot, animatingDifferences: false) } self.performSortStep() }변경사항을 적용한 Snapshot을 data source에 적용한다.
collectionView와 연결
func configureDataSource() { let cellRegistration = UICollectionView.CellRegistration <UICollectionViewCell, InsertionSortArray.SortNode> { (cell, indexPath, sortNode) in // Populate the cell with our item description. cell.backgroundColor = sortNode.color } dataSource = UICollectionViewDiffableDataSource<InsertionSortArray, InsertionSortArray.SortNode>(collectionView: insertionCollectionView) { (collectionView: UICollectionView, indexPath: IndexPath, node: InsertionSortArray.SortNode) -> UICollectionViewCell? in // Return the cell. return collectionView.dequeueConfiguredReusableCell(using: cellRegistration, for: indexPath, item: node) } let bounds = insertionCollectionView.bounds let snapshot = randomizedSnapshot(for: bounds) dataSource.apply(snapshot) }우리가 사용할 타입을 명시하고, item provider 클로저 내에서는 단순히 색을 설정해준다.
Considerations

이제
performBatchUpdates,insertItems()를 호출할 필요가 없다.Constructing Snapshots
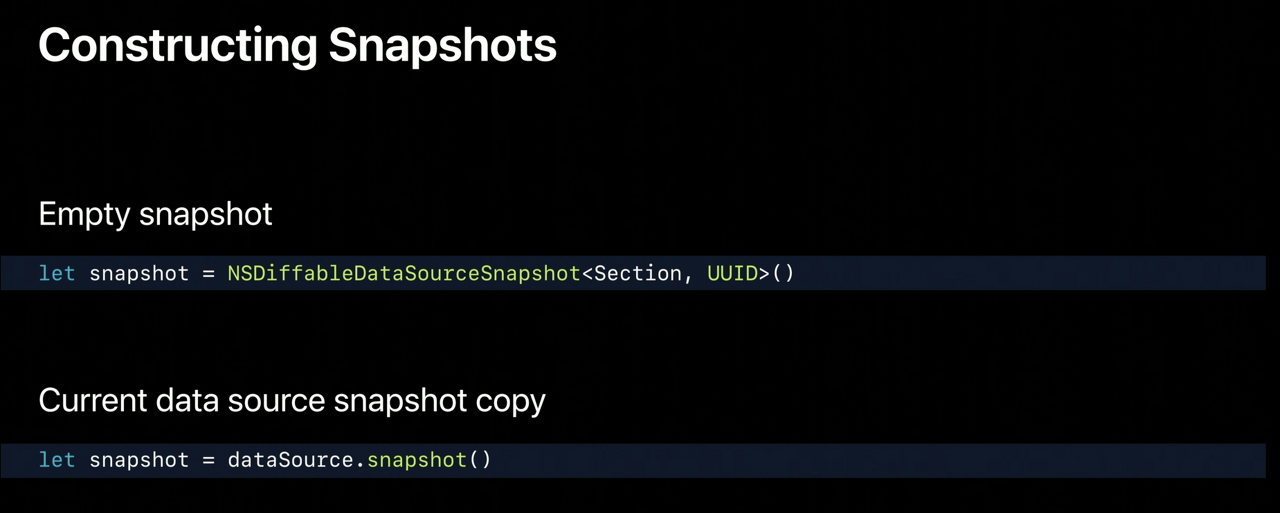
Snapshot을 생성하는 두 방법이 있다.
- 빈 Snapshot을 생성 : 섹션, 아이템으로 snapshot을 구성한다.
- 현재 상태를 나타내는 snapshot 생성 : 변경할 범위가 작을 때 유용하다. snapshot을 생성할 때, 복사본을 갖게 되기 때문에 이 snapshot에 수정작업을 해도 원본 data source에는 영향을 미치지 않는다.
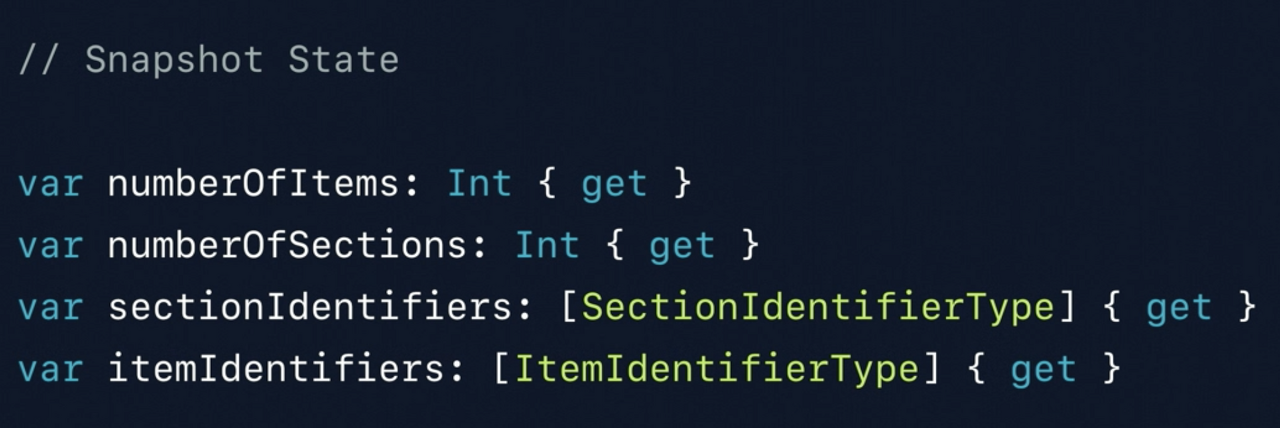
Snapshot의 아이템, 섹션이 몇 개인지, identifier가 무엇인지 알기 위한 많은 API가 있다.
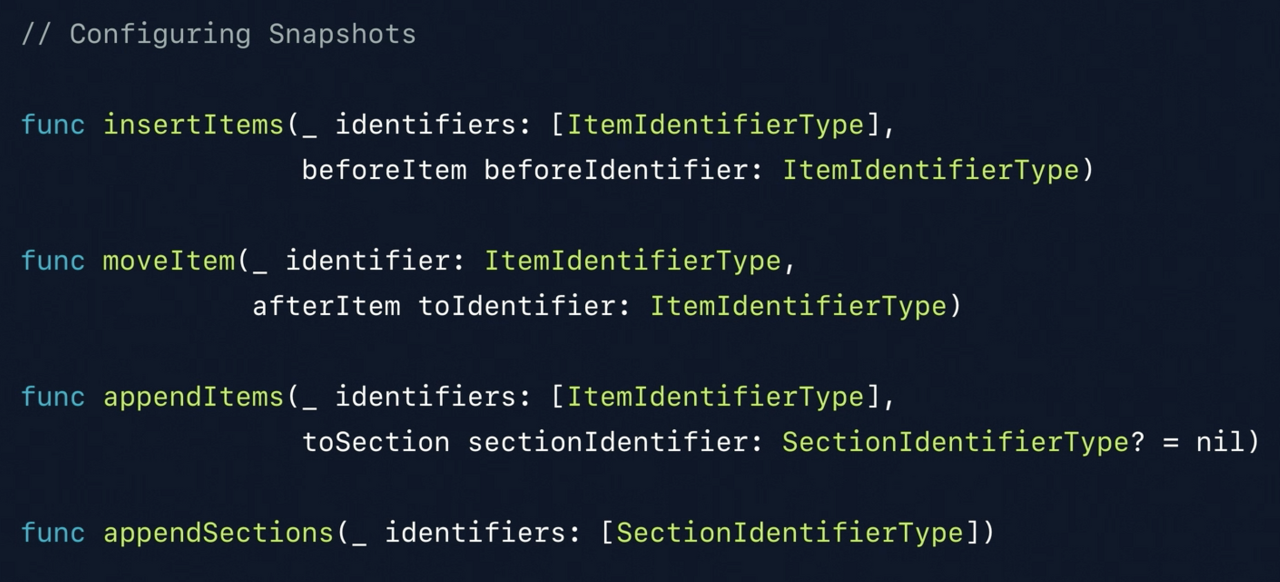
이제 IndexPath를 가지고 작업하지 않아도 되기 때문에, snapshot을 구성하는 API에서 indexPath를 사용하는 걸 확인할 수 없다.
대신 identifier를 가지고 작업한다. 가령 "a identifier" 전에 "b identifier"를 삽입하는 작업을 할 수 있다.Identifiers

- identifier는 고유해야 한다. - 대부분 앱에서 모델 객체 각각에 고유한 무언가를 부여하고 있기 때문에 고유한 identifier를 사용하는 건 자연스럽다.
- Swift에서는 hashable 해야 한다. - Swift에서는 이를 자동으로 할 수 있는 방법이 많은데, 데모에서는 enum을 사용했다.
- 모델 데이터에 identifier 자체를 추가할 수 있다.
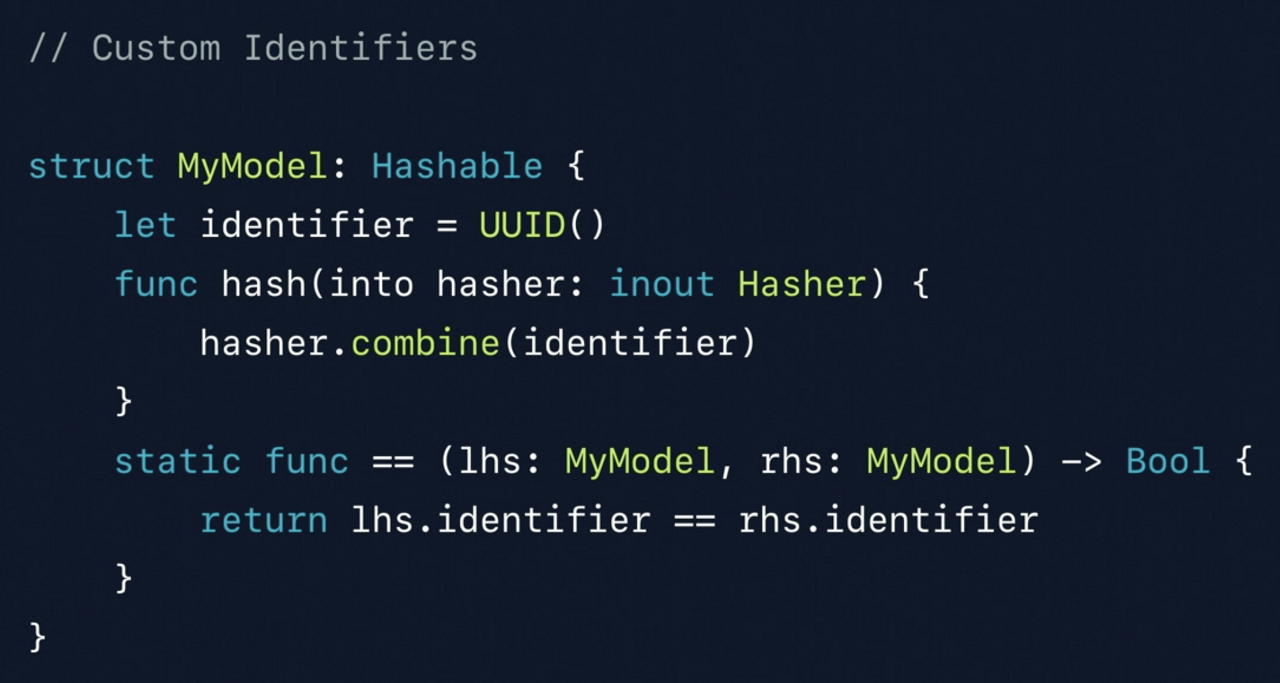
위와 같이 구조체를 이용해서 hashable 한 걸 만들 수 있다.
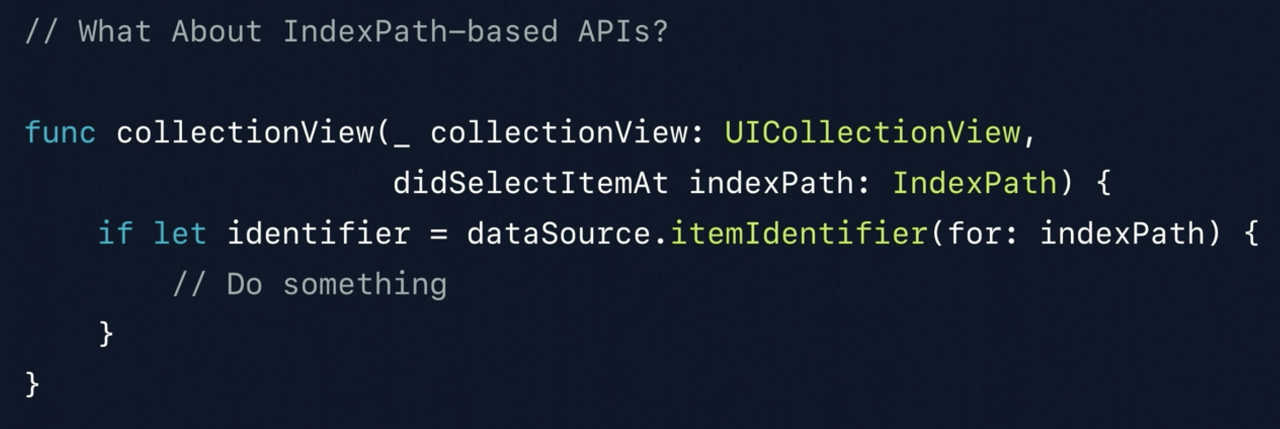
기존에 사용하던 IndexPath 기반의 API들이 있다. 이제는 indexPath 대신 identifier를 사용하고 있기 때문에 identifier와 IndexPath간 변환할 수 있는 새로운 API가 생겼다. 위 코드에서는 indexPath를 받아 이를 Identifier로 변환하고 있다. 이는 O(1) 시간 내에 할 수 있는 작업이기 때문에 굉장히 빠르다.
Performance

diff의 시간 복잡도는 O(N)이다. 따라서 아이템이 많을수록 diff는 더 오래 걸리게 된다. 앱을 개발할 때 성능을 측정하는 건 중요하다. Main queue는 항상 프리하게 해서 사용자 이벤트에 즉각적으로 반응할 수 있게 하고 싶을 것이다.
diff가 선형 시간이 걸리기 때문에 더 많은 아이템이 있을 수록 시간이 더 오래 걸린다. 따라서 apply 메서드를 백그라운드 큐에서 호출하는 건 괜찮다.

만약 모델이 백그라운드 큐에서 apply를 호출하기로 결정했다면 일관적으로 apply를 백그라운드 큐에서 호출해야 한다. 백그라운드 큐와 메인 큐에서 섞어서 호출하지 않는 것이 좋다.
정리
DiffableDataSource는 collectionView와 UITableView에 모델 데이터를 적용하는 것을 아주 간단하게 만들어준다.

간단하면서도 강력하다. 디버깅을 위해서 고생하거나 batch update 코드를 힘들게 작성하지 않아도 된다. 앱에 어떤 것을 할 것인지에만 집중할 수 있고, 복잡한 부분은 프레임워크에 맡길 수 있다.
DiffableDataSource는 iOS, TVoS, MacOS에서 사용할 수 있다. diff를 제공하는 것에 추가로 UI에 애니메이션을 통해 변화를 자연스럽게 적용할 수 있게 해준다.
내장된 diff는 빠르고, 매우 엄격하게 테스트됐다. 이를 앱에 적용하기만 하면 된다.
반응형'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
[iOS] View controller의 역할 (0) 2022.08.09 [iOS] View Controller Hierarchy - 뷰 컨트롤러 계층 구조 (0) 2022.08.09 [WWDC22] Design App Shortcuts (0) 2022.06.20 [WWDC22] Complications and widgets: Reloaded (0) 2022.06.17 [WWDC22] Design protocol interfaces in Swift (0) 2022.06.16
